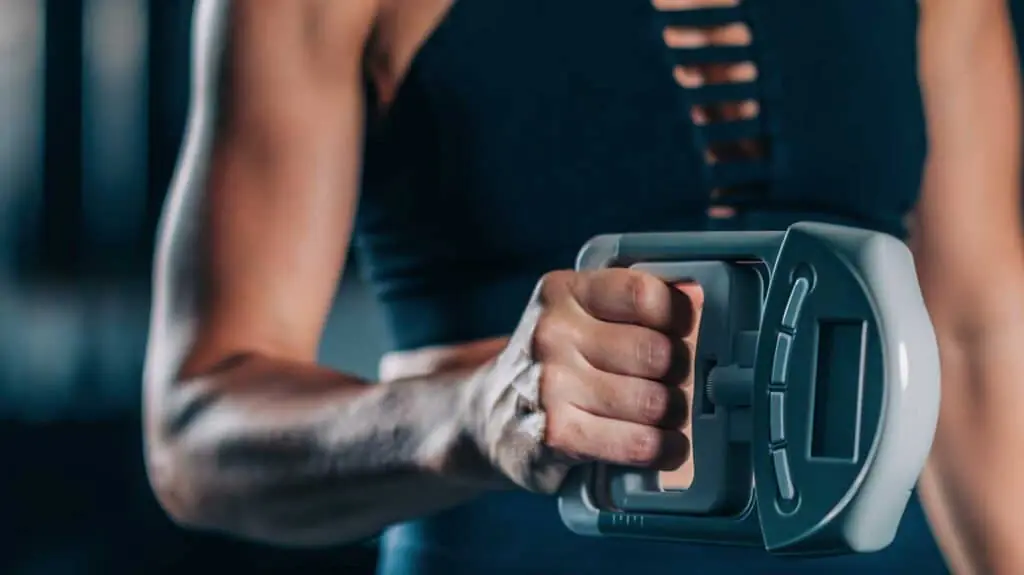
Grip strength is one of the strongest predictors of longevity. Does that mean squeezing a stress ball will make you live longer? Not necessarily. Grip strength serves as a proxy for overall upper body strength and muscle mass, both of which play a crucial role in metabolic health, function, and long-term independence. Research shows that weaker grip strength is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, frailty, and early mortality, making it a critical health marker.
A decline in grip strength is often a flag for broader issues, including muscle loss (sarcopenia), reduced neuromuscular function, and metabolic decline. A weak grip doesn’t directly cause death, but it correlates with conditions that do. When muscle strength diminishes, physical activity declines, leading to reduced cardiovascular health, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of falls and injury. Because of this, grip strength is now considered a biomarker for overall health.
The Science Behind Grip Strength and Longevity
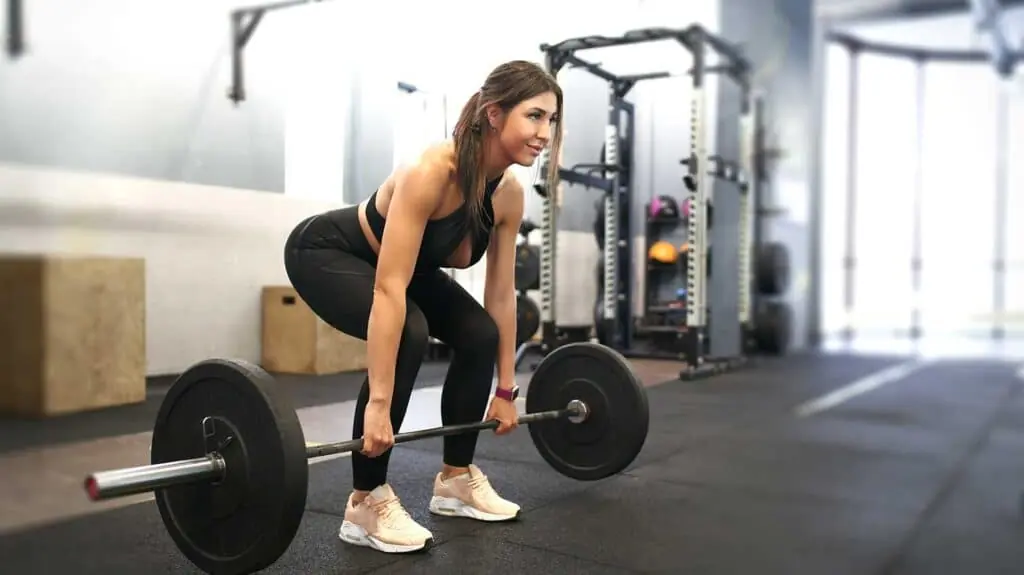

Research consistently shows that grip strength is more than just a measure of hand function, it serves as a powerful predictor of overall health, disability risk, and mortality. Studies have linked weaker grip strength to higher rates of chronic disease, loss of independence, and even early death.
- One study found that each 5kg decrease in grip strength was associated with a 16% higher risk of all-cause mortality and a 21% increased risk of cardiovascular mortality, independent of other health factors.
- A meta-analysis of 42 studies found that individuals with low grip strength had a 67% higher risk of early death from all causes compared to those with high grip strength.
- In older adults, grip strength predicts disability risk more accurately than age alone. Those with the lowest grip strength categories are more likely to experience loss of independence and require assistance with daily activities.
- Grip strength has been associated with longevity better than blood pressure in some studies.
What Grip Strength Really Represents
- Muscle Mass and Strength – Strong grip correlates with higher lean muscle mass, which is protective against metabolic diseases and sarcopenia.
- Neuromuscular Function – Grip strength reflects motor unit recruitment, which declines with age and contributes to weakness and mobility issues.
- Functional Independence – Higher grip strength is linked to better ability to perform daily tasks like lifting objects, opening jars, and maintaining balance.
- Frailty Risk – Low grip strength is part of the Frailty Index, a clinical measure used to assess vulnerability in older adults. Those with declining grip strength are at higher risk of hospitalization and loss of mobility.
How to Test Grip Strength
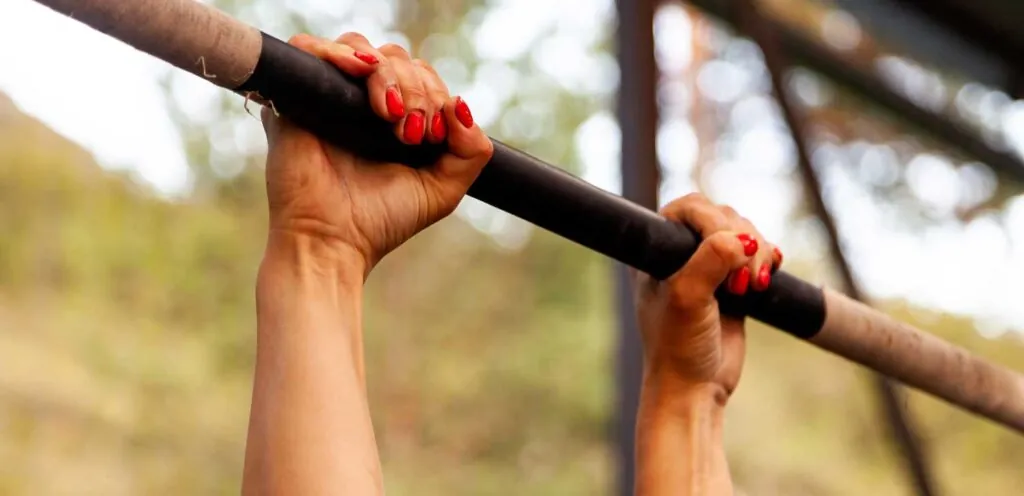

Grip strength is a key indicator of overall physical health and can impact everything from daily activities to athletic performance. Here are three effective ways to test grip strength:
- Dynamometer Test – The gold standard for measuring grip strength, where individuals squeeze a handheld device to assess force output. Grip strength norms vary by age and sex, but in general, men should aim for 110+ lbs and women for 65+ lbs to fall within the healthy range.
- Hanging Time Test – A simple but effective method where participants hang from a pull-up bar for as long as possible. Adults should aim for at least 1 minute.
- Functional Strength Indicators – Exercises like farmer’s carries, deadlifts, and pull-ups indirectly assess grip endurance and total upper body strength.
How to Improve Grip Strength
Since grip strength is a marker for total upper body strength, the best way to improve it is through compound movements that engage the forearms, hands, and major muscle groups:
- Deadlifts – Develops grip strength by requiring the hands to maintain a firm hold on heavy loads. Additionally, it improves posterior chain strength, which supports posture and overall power.
- Pull-Ups/Chin-Ups – Builds forearm and hand strength while reinforcing back and arm muscle development. A strong pull-up performance is one of the best functional indicators of upper body strength.
- Rows – Improves pulling power and grip endurance, particularly when performed with controlled negatives.
- Farmer’s Carry – A direct test and training method for grip endurance, requiring sustained force production over time. Carrying bodyweight-equivalent loads for 30+ seconds is an excellent performance goal.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Grip Strength
Physical therapy plays an important role in maintaining and improving grip strength, especially for those recovering from injuries or those who don’t know where to start. Here’s how PTs can help:
- Addressing Strength & Mobility Deficits– Physical therapists can assess for movement deficits and prescribe interventions to improve function.
- Modifying Training for Injuries – If joint pain or past injuries limit grip strength or training, PTs can adjust programming to maintain muscle mass and protect injured areas.
- Provide Personalized Plan – Every person requires a different approach; your PT will be able to prescribe the exercises that best fit your needs.
Key Takeaways
Grip strength is a powerful indicator of overall health, muscle function, and longevity. It reflects upper body strength and plays a crucial role in maintaining independence and reducing health risks.
- Grip strength is one of the strongest longevity predictors.
- Squeezing things doesn’t make you live longer, but grip strength reflects overall upper body muscle mass and strength.
- The best way to improve grip strength is through strength training.
- Physical therapy can help guide you in a personalized, pain-free strength-training program.
If you’re experiencing weakness, pain, or want to improve your strength, tap below to schedule a session with a physical therapist and take the next step toward improved longevity.
Physical Therapy Near You
Given the frequent use of shoulders in various daily activities, paying attention to any unusual sensations in the joint is crucial. Whether you’re experiencing chronic shoulder pain or occasional discomfort, seeking treatment from a qualified physical therapist is essential for adequate recovery, and regular sessions with a physical therapist can significantly improve your mobility, reduce pain, and enhance your overall quality of life. Take the first step towards recovery by finding a physical therapy location near you. Early intervention can lead to quicker and more effective relief, allowing you to return to normal activities and get back to what you love.


