[tsf_breadcrumb sep="/" class="breadcrumbs]
Home / Patients / Primary Services / Motor Vehicle Accidents (MVA)
Recovering from a motor vehicle accident (MVA) is a journey, but you don’t have to do it alone. From minor strains to more severe injuries, our physical therapy focuses on getting you back to your best self. We’ll develop exercises to help you regain strength and mobility, offering pain relief strategies that fit your life. Together, we’ll work toward getting you back to normal as quickly and safely as possible.
Motor vehicle accidents (MVAs) can lead to a wide range of injuries that impact mobility, function, and quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores the vital role of physical therapy (PT) in the recovery process after a MVA. Readers will learn how targeted therapy techniques and personalized exercise programs can reduce pain, restore movement, and support long-term healing. Whether you’re recovering from an accident, exploring treatment options, or a healthcare professional looking to better understand the benefits of PT, this resource offers valuable insights to help guide effective recovery and rehabilitation.

After a MVA, it can be difficult to understand the source and extent of your pain. Thanks to direct access laws in many states, you can see a PT without first visiting your doctor, making it easier and faster to address post accident related symptoms such as pain or stiffness. PTs are trained to screen for serious injuries and will refer you to a physician if additional evaluation or diagnostic testing is needed, so seeing a PT first is both safe and effective for long-term recovery.
PTs use a combination of clinical assessments and diagnostic tools to evaluate injuries sustained in a MVA. This includes reviewing your medical history, assessing posture, ROM, strength and flexibility, as well as performing functional movement tests to identify areas of dysfunction. PTs may also review imaging results if available such as, X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans, to guide treatment. By carefully evaluating the location and nature of pain, PTs can develop a personalized rehabilitation plan focused on restoring mobility, reducing pain, and preventing long-term complications.
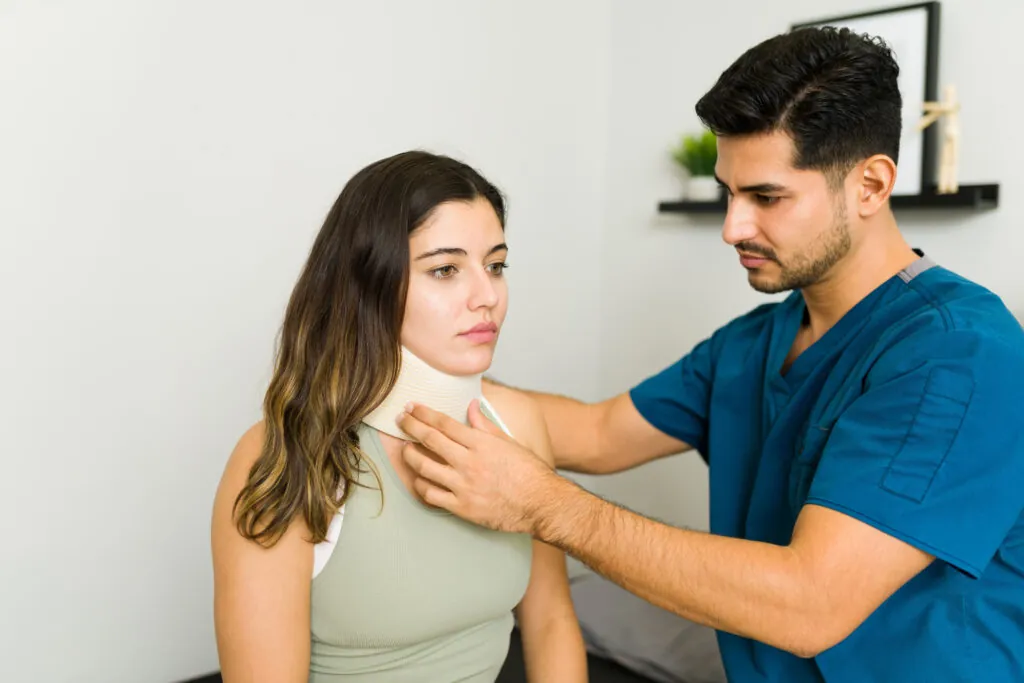
MVAs can cause a wide range of injuries, from whiplash and soft tissue damage to fractures and chronic pain. PT is an effective way to restore function, reduce pain, and prevent long-term complications after such accidents. Through targeted rehabilitation, PTs help patients regain strength, mobility, and confidence in their daily activities.
When you begin PT after an accident, a thorough initial assessment is conducted. At Confluent Health, this includes a detailed review of your medical history, an evaluation of your pain and functional limitations, and specialized tests to identify joint, muscle, or nerve involvement. This assessment allows therapists to develop a personalized, patient centered treatment plan tailored to your unique injuries and recovery goals.
PTs use a variety of methods to address common MVA-related injuries, some of which include:
The primary goals of PT are to reduce pain and inflammation, restore mobility, improve strength, and promote overall functional independence. It also helps to prevent future injuries or the development of chronic pain while supporting your long-term recovery and quality of life. Since every individual’s injuries and needs are different, PTs create personalized treatment plans tailored to the type and severity of your injury, your daily activity requirements, and your specific recovery goals. This individualized approach ensures that each session is safe, effective, and focused on helping you return to your prior level of function.
Physical therapy can help focus on restoring your mobility, strength, tolerance to activity, and overall function.
Whiplash, neck pain, back pain, shoulder pain, joint stiffness, fear of driving, and many other symptoms are common following a car accident. Your physical therapist can help identify these symptoms and work towards alleviating them.
It is best to begin PT as soon as possible. Early intervention helps reduce stiffness, restore mobility, and prevent chronic pain or compensatory movement patterns from developing.
Yes. Targeted exercises, manual therapy, and posture training can reduce pain, improve neck and back mobility, and promote tissue healing after whiplash. Consistent PT also helps retrain muscles and joints to move safely, reducing the risk of long-term discomfort.
Recovery time varies based on the severity of the injury and individual healing factors, however many people notice improvement within a few weeks of consistent treatment. More complex injuries or long-standing symptoms may require several months or PT to fully restore strength and function.