[tsf_breadcrumb sep="/" class="breadcrumbs]
Home / Patients / Primary Services / Orthopedics
When it comes to musculoskeletal issues, you’re in expert hands. Our orthopedic specialists are highly trained in diagnosing and treating conditions affecting your bones, joints, and muscles. Whether it’s a sports injury, arthritis, or post-surgical recovery, we’re here to help you regain function and mobility. We use cutting-edge techniques and evidence-based practices to ensure you get the best care possible. Working together, we’ll help you overcome pain, restore movement, and get back to doing what you love.
Orthopedic pain- whether from injury, overuse, or chronic conditions- can significantly impact one’s mobility, independence, and overall quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores the vital role of physical therapy (PT) in managing and recovering from orthopedic pain, offering readers evidence-based insight into effective treatment strategies, from personalized exercise programs to manual therapy techniques and pain relief modalities, PT provides a pathway to improved function and lasting relief. The following content is designed to inform individuals seeking treatment options, patients interested in understanding the benefits of PT, and referring healthcare professionals looking to enhance care coordination for orthopedic pain management.
Orthopedic pain encompasses discomfort originating from the musculoskeletal system, including bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. This type of pain can result from acute injuries, overuse, degenerative conditions, inflammatory diseases or post surgical recovery.1 Common examples include osteoarthritis, fractures, sprains, and tendonitis.
Globally, approximately 1.71 billion people suffer from musculoskeletal conditions making them the leading contributor to disability worldwide.1 Low back pain alone affects 570 million individuals and accounts for 7.4% of global years lived with disability.1 Women report musculoskeletal pain more frequently than men, but men often experience more persistent pain. Additionally, individuals with a higher body mass index (BMI) are about twice as likely to experience musculoskeletal pain compared to those with a lower BMI.2
Orthopedic pain can significantly affect daily activities and overall quality of life. Basic movements such as walking, climbing stairs, or sitting in low chairs can become challenging or impossible due to pain. Chronic pain is associated with increased rates of anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances.3 The constant discomfort can lead to feelings of helplessness and decreased emotional well-being. Individuals may withdraw from social engagements and hobbies, leading to isolation. Work productivity can decline, and some may be forced to retire early or reduce working hours due to pain.4 The financial strain that this can cause one to endure includes direct costs such as medical expenses and indirect costs such as lost wages and decreased productivity.
PT plays a crucial role in managing orthopedic pain. Through targeted exercises and modalities, physical therapists (PTs) can help reduce pain and inflammation, Therapists design personalized rehabilitation programs to improve mobility, strength, and flexibility, aiding in the recovery of daily functions, Education on posture, body mechanics, and ergonomics helps prevent future injuries. By addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of pain, PT improves overall quality of life and helps individuals regain independence.4
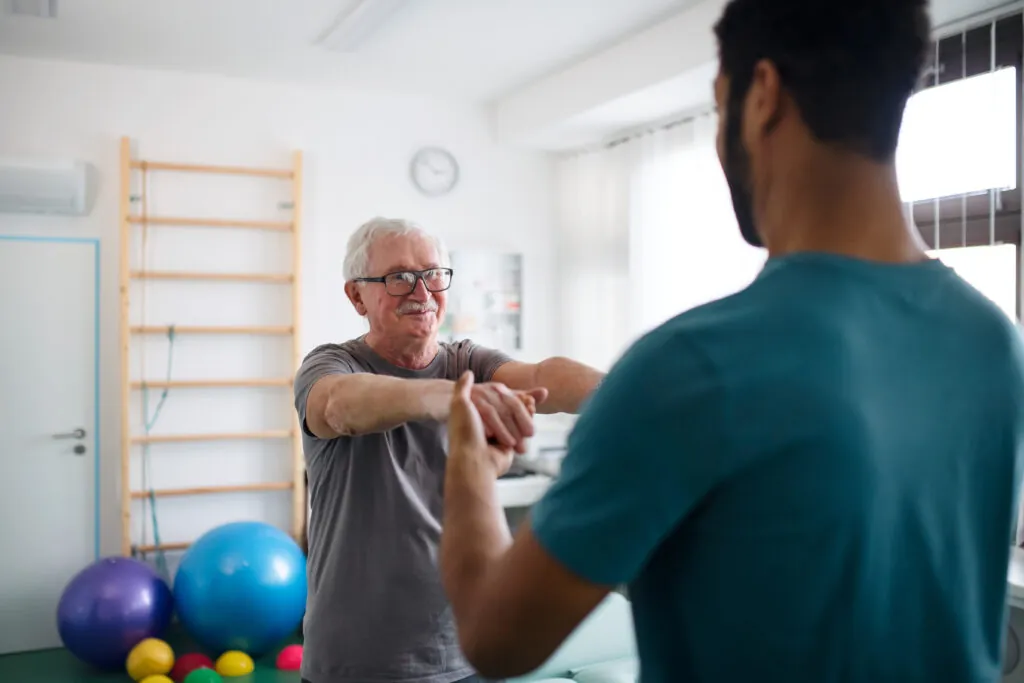

Preventing orthopedic pain starts with maintaining strong, flexible, and balanced muscles and joints. Regular strengthening and flexibility exercises help support proper alignment, improve stability, and reduce the risk of injury. Maintaining a healthy weight lessens stress on joints, especially in the hips, knees, and spine. Finally, listening to your body’s signals- such as pain, stiffness, or fatigue and testing when needed can prevent minor issues from becoming chronic problems. Consistent attention to these habits goes a long way in preserving joint health and overall mobility.
Living with orthopedic pain can be challenging, but the right coping strategies and support can make a significant difference in quality of life. Incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, gentle stretching, meditation, or yoga can help reduce muscle tension and ease discomfort. Seeking psychological support through counseling, support groups, or mindfulness based therapies can also help manage the emotional impact of chronic pain.
A personalized treatment plan is essential for long-term success. Every individual’s pain experience is different, and a plan tailored to your specific condition, lifestyle, and goals ensures the most effective and sustainable results.
If you’re struggling with ongoing pain, it’s important to seek professional guidance from a PT, orthopedic specialist, or pain management provider. Early and consistent care not only helps relieve symptoms but also promotes long-term health, mobility, and overall well-being.
PT is one of the most effective ways to manage orthopedic pain by addressing the root causes and restoring function. Through personalized care, PTs help reduce pain, improve movement, and prevent future injury. In the realm of how PTs evaluate orthopedic pain, the process is methodical and multi-layered. The initial PT eval typically lasts about 30-60 minutes, during which the therapists will gather a thorough history (symptom onset, provocative factors, prior treatments, activity limitations) and perform a physical examination.
During the physical scan, the PT will assess the following:
Based on all of these assessments, the PT is able to develop a diagnosis or working hypothesis that allows them to develop a plan of care including goals, interventions, manual therapy, as well as strength and mobility exercises. Common PT interventions include manual therapy, which involves joint mobilization and soft tissue techniques, as well as targeted exercises that build strength and flexibility. Functional training is also a key component and works to improve posture and movement patterns. Therapists also use modalities such as heat or cold therapy, electrical stimulation, or dry needling to decrease pain and promote healing.
Because every case of orthopedic pain is different, PTs design individualized treatment plans that are tailored to each patient’s condition, lifestyle, and goals. The overarching goal of a PT session is to reduce pain and inflammation, restore mobility and strength, and teach proper body mechanics to support long-term recovery, while keeping the unique goals of the individual at the center of care.
Recovery time can vary widely depending on the specific condition and individual factors, but your PT will tailor the treatment plan to your recovery goals.
Persistent pain, joint stiffness, muscle weakness, or decreased function are all indicators that PT might be beneficial.
Orthopedic pain is caused by issues within the musculoskeletal system, including bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Common causes include injuries (such as fractures or sprains), overuse or repetitive strain, and degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis. Lifestyle factors, such obesity, can also contribute.
Diagnosis typically begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination. Next, imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may be used to identify structural problems, which blood tests can help detect inflammatory or autoimmune causes. PTs may also assess movement patterns to pinpoint sources of pain.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause but often includes a combination of rest, PT, medications, and lifestyle modifications. PT is a cornerstone, focusing on pain relief, improving mobility, and strengthening muscles to prevent future injury. In more severe cases, interventions like injections or surgery may be necessary.